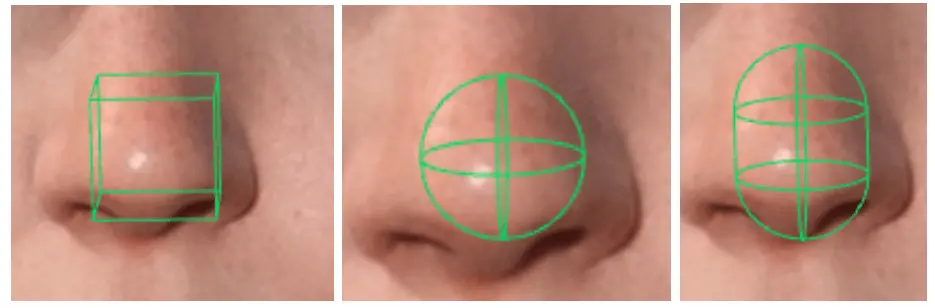
Physics Mechanics
Rundown of the physics engine available in DeepAR
DeepAR 4.0 introduces physics components that allow you to build simple physics simulations. This functionality is still in beta and some bugs might be present. We recommend you save your effects frequently.
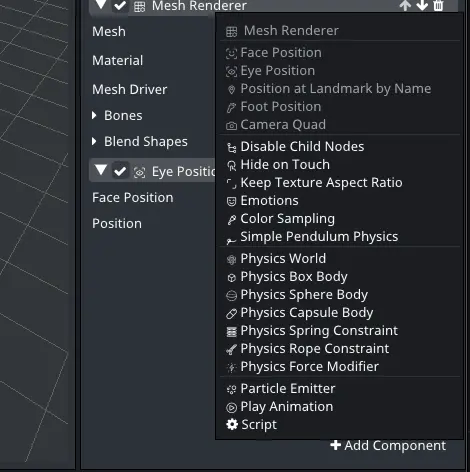
The new physics components can be found in the right panel under Properties.
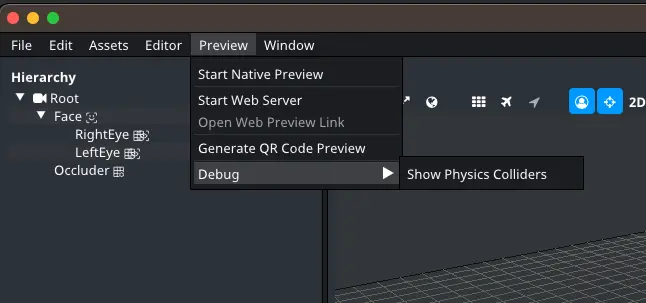
The debug option can be found in the top bar menu under Preview.
Physics World
Controls the child and descendant physics objects. This component must be added to an ancestor node in order for the simulation to run.
Parameters:
Gravity
- the force representing gravity in world space (positive Y is down)
Kinematic Knockback Factor
- multiplier of an impulse which will be applied by static physics bodies to non-static physics bodies with which they collide
- setting this value to 0 will disable the knockback.
Enable Simulation
- enable/disable physics simulation
- setting this value to false will behave the same as if no physics world was added
Physics objects that are assigned to different physics worlds will NOT interact with each other.
Physics Body
Adding any Physics body component to a game object will put its motion under the control of the ancestor Physics world.

Physics body components differ in the shape of their colliders.
The default colliders have fixed rotation values - if added to the object itself, they inherit the position, but not the other properties.
Physics Box Body
A physics body with a box collider.
Parameters:
Static Body
static body objects are not controlled by physics but do interact with other physics body objects
static body objects implicitly have zero mass
Solid Body
- solid body objects will collide with other solid body objects
- making bodies non-solid can be useful for detecting collisions, but not responding to them
Restitution
- coefficient representing the elastic collision ratio for a certain object
Mass
the mass of a body object
zero mass implies static body object
Ignore gravity
- controls if the object is affected by gravity
- other forces will still move the body object
Fixed Position
- physics does not affect the position of the body object in the axes that are fixed
Fixed Rotation
- physics does not affect the rotation of the body object in the axes that are fixed
Extent
- X, Y, and Z sizes of the collider
Physics Sphere Body
A physics body with a sphere collider.
Parameters:
Static Body, Solid Body, Mass, Ignore Gravity, Fixed Position, Fixed Rotation, Restitution
- same as the Physics Box Body
Radius
- radius of the sphere
Physics Capsule Body
A physics body with a capsule collider.
Parameters:
Static Body, Solid Body, Mass, Ignore Gravity, Fixed Position, Fixed Rotation, Restitution
- same as the Physics Box Body
Radius
- radius of the capsule
Height
the height of the cylinder between two half spheres
height of 0 makes this the same as a sphere collider
Contraints
Logical building block components which will allow you to create a constraint link between the current game object and the parent game object, both of which must have a physics body component.

Physics Spring Constraint
Spring constraint between the two linked physics bodies.
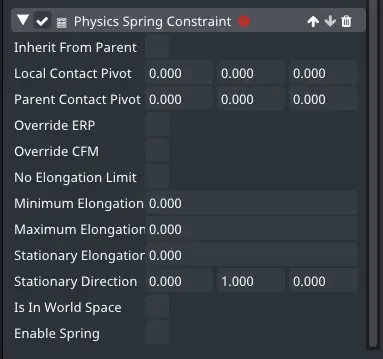
Parameters:
Inherit From Parent
- when a parent body also has a physics constraint of the same type as its parent, you can check this option to inherit the same parameters (making the setup a lot easier for chains where each element has the same properties)
Local Contact Pivot
- offset of the constraint contact point from the current object (in current object local space)
Parent Contact Pivot
- offset of the constraint contact point from the parent object (in parent object local space)
Override ERP
- Error reduction parameter
Override CFM
- Constraint force mixing
No Elongation Limit
- disables minimum and maximum elongation limit of the spring (the spring can be infinitely compressed and expanded)
Minimum Elongation
- length of the spring when maximally compressed
Maximum Elongation
- length of the spring when maximally expanded
Stationary Elongation
length of the spring when in equilibrium
the spring will oscillate around this point
Stationary Direction
- the direction in which the spring expands
Is In World Space
- if checked, the Stationary Direction is in world space, otherwise, it is in the parent body’s local space
Enable Spring
- enables/disables the spring
Physics Rope Constraint
Rope constraint between the two linked physics bodies.
Parameters:
Inherit From Parent, Local Contact Pivot, Parent Contact Pivot, Override ERP, Override CFM
- same as the Physics Spring Constraint
Rope Length
length of the rope
Modifiers
Physics Force Modifier
Allows a constant directional force to be added to a Physics body.
Parameters:
Enable Modifier
enable/disable physics modifier
setting this value to false will behave the same as if no physics force modifier was added
Apply To Children
- apply force to child game objects (shallow)
Force
- force vector
Is In World Space
- if true the force vector is in world space, otherwise it is in the game objects local space
Scale by mass
- scales the force by the mass of the physics body (so the specified force will behave as if it was acceleration instead)
Debug
Options for debugging and setting up physics.

Simulate physics
If disabled physics will not be simulated, useful for setting up a scene, especially if there are multiple physics world components in the scene.
Show Colliders
Shows the wireframe colliders of physics body objects as well as the pivot points of the constraint objects.